17 KiB
17 KiB
驱动
驱动基础知识
内核源码编译过程
1.遍历每个源码目录(或配置指定的源码目录)Makefile
2.每个目录的Makefile 会根据Kconfig来定制要编译对象
3.回到顶层目录的Makeifle执行编译
Kconfig ---> (每个源码目录下)提供选项 (决定哪些需要编译那些不需要)
.config ---> (源码顶层目录下)保存选择结果 (默认配置)
Makefile---> (每个源码目录下)根据.config中的内容来告知编译系统如何编译
举例
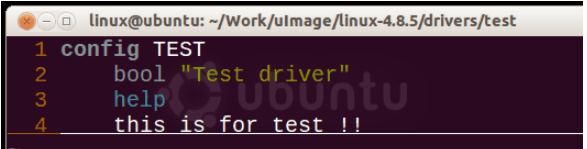
第一步:配置Kconfig
在driver目录下新建一个目录,
mkdir driver/test
进入test目录,创建Kconfig文件
这里定义了一个TEST的句柄,Kconfig可以通过这个句柄来控制Makefile中是否编译,”Test driver”是显示在终端的名称
第二步:配置Makefile
Obj-$(CONFIG_选项名) += xxx.o /当CONFIG_选项名=y时,表示对应目录下的xxx.c将被编译进内核 当CONFIG_选项名=m时对应目录下的xxx.c将被编译成模块/
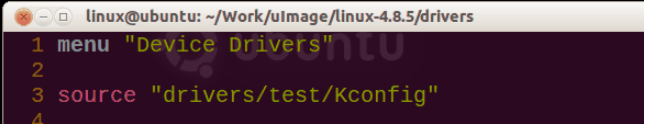
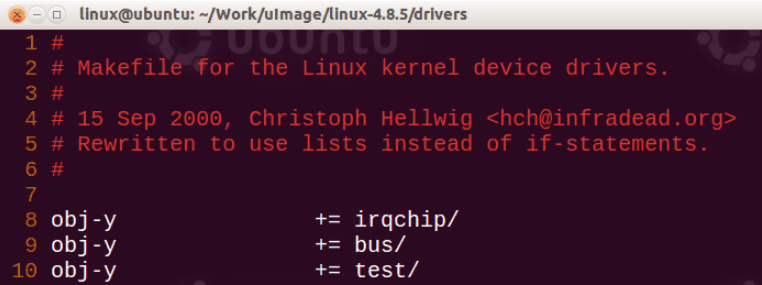
第三步 配置上层目录的Makefile与Kconfig
在上一层目录的Kconfig中
在上一层目录的Makefile中
结果,运行根目录的.config查看结果
驱动程序分析过程
插入驱动
- insmod chrdevbase.ko
- 输入“lsmod”命令即可查看当前系统中存在的模块
- cat /proc/devices 查看当前系统中所有的设备
- 驱动加载成功需要在/dev 目录下创建一个与之对应的设备节点文件,应用程序就是通过操
作这个设备节点文件来完成对具体设备的操作,使用旧接口注册的驱动需要用命令创建设备节点
- mknod /dev/chrdevbase c 200 0
驱动加载进内核或以模块插入后会运行下面的初始化接口
subsys_initcall(); //用于核心子系统的初始化,初始化时间早于module_init
module_init(); //适用于以模块形式编译的代码,insmod加载驱动时会调用这个函数
module_exit();
初始化接口里进行设备驱动的注册
注册函数
- 对于字符设备驱动:
- register_chrdev() - 注册字符设备号 //旧方法,需要手动创建设备节点
- cdev_add() - 添加cdev结构到系统 //新方法, 会自动创建设备节点
- 对于平台驱动:
- platform_driver_register() - 注册平台驱动
- 对于I2C和SPI总线驱动:
- i2c_add_driver() - 注册I2C驱动
- spi_register_driver() - 注册SPI驱动
- 对于USB驱动:
- usb_register() - 注册USB驱动
- 对于网络设备驱动:
- register_netdev() - 注册网络接口
- 通用设备驱动注册:
- driver_register() - 注册设备驱动
- PCI设备驱动:
- pci_register_driver() - 注册PCI设备驱动
- 输入设备驱动:
- input_register_device() - 注册输入设备
字符设备
字符设备框架
静态注册设备
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/ide.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/gpio.h>
#include <asm/mach/map.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
#define LED_MAJOR 200 /* 主设备号 */
#define LED_NAME "led" /* 设备名字 */
static int led_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
return 0;
}
static ssize_t led_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t cnt, loff_t *offt)
{
return 0;
}
static ssize_t led_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t cnt, loff_t *offt)
{
return 0;
}
static int led_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
return 0;
}
static struct file_operations led_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = led_open,
.read = led_read,
.write = led_write,
.release = led_release,
};
static int __init led_init(void)
{
register_chrdev(LED_MAJOR, LED_NAME, &led_fops);
return 0;
}
static void __exit led_exit(void)
{
unregister_chrdev(LED_MAJOR, LED_NAME);
}
module_init(led_init);
module_exit(led_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("sakura");
static inline int register_chrdev(unsigned int major, const char *name,const struct file_operations *fops)
major:主设备号,Linux 下每个设备都有一个设备号,设备号分为主设备号和次设备号两部分
name:设备名字,指向一串字符串。
fops:结构体 file_operations 类型指针,指向设备的操作函数集合变量。
新字符设备,引用了字符设备结构体
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/ide.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/gpio.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <asm/mach/map.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
/* newchrled设备结构体 */
struct newchrled_dev{
dev_t devid; /* 设备号 */
struct cdev cdev; /* cdev */
struct class *class; /* 类 */
struct device *device; /* 设备 */
int major; /* 主设备号 */
int minor; /* 次设备号 */
};
struct newchrled_dev newchrled; /* led设备 */
static int led_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
filp->private_data = &newchrled; /* 设置私有数据 */
return 0;
}
static ssize_t led_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t cnt, loff_t *offt)
{
return 0;
}
static ssize_t led_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t cnt, loff_t *offt)
{
return 0;
}
static int led_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
return 0;
}
/* 设备操作函数 */
static struct file_operations newchrled_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = led_open,
.read = led_read,
.write = led_write,
.release = led_release,
};
static int __init led_init(void)
{
if (newchrled.major) { /* 定义了设备号 */
newchrled.devid = MKDEV(newchrled.major, 0);
register_chrdev_region(newchrled.devid, NEWCHRLED_CNT, NEWCHRLED_NAME);
} else { /* 没有定义设备号 */
alloc_chrdev_region(&newchrled.devid, 0, NEWCHRLED_CNT, NEWCHRLED_NAME); /* 申请设备号 */
newchrled.major = MAJOR(newchrled.devid); /* 获取分配号的主设备号 */
newchrled.minor = MINOR(newchrled.devid); /* 获取分配号的次设备号 */
}
newchrled.cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
cdev_init(&newchrled.cdev, &newchrled_fops);
cdev_add(&newchrled.cdev, newchrled.devid, NEWCHRLED_CNT);
newchrled.class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, NEWCHRLED_NAME);
newchrled.device = device_create(newchrled.class, NULL, newchrled.devid, NULL, NEWCHRLED_NAME);
return 0;
}
static void __exit led_exit(void)
{
cdev_del(&newchrled.cdev);/* 删除cdev */
unregister_chrdev_region(newchrled.devid, NEWCHRLED_CNT); /* 注销设备号 */
device_destroy(newchrled.class, newchrled.devid);
class_destroy(newchrled.class);
}
module_init(led_init);
module_exit(led_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("zuozhongkai");
platform驱动
- i2c,spi等都属于此类驱动,i2c控制器驱动和spi控制器驱动就相当于platform驱动,通过core注册。
i2c和spi设备分别可通过内核态或者用户态控制。platform驱动匹配过程->driver_register->bus_add_driver
->driver_attach->__driver_attach->device_driver_attach->driver_probe_device->really_probe-> drv->probe(dev) 或者 dev->bus->probe(dev)
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/ide.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/gpio.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
#include <linux/semaphore.h>
#include <linux/timer.h>
#include <linux/irq.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/fcntl.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <asm/mach/map.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
struct leddev_dev{
dev_t devid; /* 设备号 */
struct cdev cdev; /* cdev */
struct class *class; /* 类 */
struct device *device; /* 设备 */
int major; /* 主设备号 */
};
struct leddev_dev leddev; /* led设备 */
static int led_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
filp->private_data = &leddev; /* 设置私有数据 */
return 0;
}
static ssize_t led_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t cnt, loff_t *offt)
{
return 0;
}
static struct file_operations led_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = led_open,
.write = led_write,
};
static int led_probe(struct platform_device *dev)
{
if (leddev.major) { /* 定义了设备号 */
leddev.devid = MKDEV(leddev.major, 0);
register_chrdev_region(leddev.devid, LEDDEV_CNT, LEDDEV_NAME);
} else { /* 没有定义设备号 */
alloc_chrdev_region(&leddev.devid, 0, LEDDEV_CNT, LEDDEV_NAME); /* 申请设备号 */
leddev.major = MAJOR(leddev.devid); /* 获取分配号的主设备号 */
}
leddev.cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
cdev_init(&leddev.cdev, &led_fops);
cdev_add(&leddev.cdev, leddev.devid, LEDDEV_CNT);
leddev.class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, LEDDEV_NAME);
leddev.device = device_create(leddev.class, NULL, leddev.devid, NULL, LEDDEV_NAME);
return 0;
}
static int led_remove(struct platform_device *dev)
{
cdev_del(&leddev.cdev);/* 删除cdev */
unregister_chrdev_region(leddev.devid, LEDDEV_CNT); /* 注销设备号 */
device_destroy(leddev.class, leddev.devid);
class_destroy(leddev.class);
return 0;
}
static struct platform_driver led_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "imx6ul-led", /* 驱动名字,用于和设备匹配 */
},
.probe = led_probe,
.remove = led_remove,
};
static int __init leddriver_init(void)
{
return platform_driver_register(&led_driver);
}
static void __exit leddriver_exit(void)
{
platform_driver_unregister(&led_driver);
}
module_init(leddriver_init);
module_exit(leddriver_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("zuozhongkai");
dts的platform驱动
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/ide.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/gpio.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
#include <linux/semaphore.h>
#include <linux/timer.h>
#include <linux/irq.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/fcntl.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <asm/mach/map.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
struct leddev_dev{
dev_t devid; /* 设备号 */
struct cdev cdev; /* cdev */
struct class *class; /* 类 */
struct device *device; /* 设备 */
int major; /* 主设备号 */
struct device_node *node; /* LED设备节点 */
int led0; /* LED灯GPIO标号 */
};
struct leddev_dev leddev; /* led设备 */
static int led_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
filp->private_data = &leddev; /* 设置私有数据 */
return 0;
}
static struct file_operations led_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = led_open,
.write = led_write,
};
static int led_probe(struct platform_device *dev)
{
if (leddev.major) {
leddev.devid = MKDEV(leddev.major, 0);
register_chrdev_region(leddev.devid, LEDDEV_CNT, LEDDEV_NAME);
} else {
alloc_chrdev_region(&leddev.devid, 0, LEDDEV_CNT, LEDDEV_NAME);
leddev.major = MAJOR(leddev.devid);
}
cdev_init(&leddev.cdev, &led_fops);
cdev_add(&leddev.cdev, leddev.devid, LEDDEV_CNT);
leddev.class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, LEDDEV_NAME);
leddev.device = device_create(leddev.class, NULL, leddev.devid, NULL, LEDDEV_NAME);
leddev.node = of_find_node_by_path("/gpioled");
of_get_named_gpio(leddev.node, "led-gpio", 0);
return 0;
}
static int led_remove(struct platform_device *dev)
{
cdev_del(&leddev.cdev); /* 删除cdev */
unregister_chrdev_region(leddev.devid, LEDDEV_CNT); /* 注销设备号 */
device_destroy(leddev.class, leddev.devid);
class_destroy(leddev.class);
return 0;
}
static const struct of_device_id led_of_match[] = {
{ .compatible = "atkalpha-gpioled" },
{ /* Sentinel */ }
};
static struct platform_driver led_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "imx6ul-led", /* 驱动名字,用于和设备匹配 */
.of_match_table = led_of_match, /* 设备树匹配表 */
},
.probe = led_probe,
.remove = led_remove,
};
static int __init leddriver_init(void)
{
return platform_driver_register(&led_driver);
}
static void __exit leddriver_exit(void)
{
platform_driver_unregister(&led_driver);
}
module_init(leddriver_init);
module_exit(leddriver_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("zuozhongkai");
驱动程序注册重要函数
设备树
- 设备树的作用:描述板级信息
- 设备树路径一般在arch目录下 例如:kernel_t41/kernel-4.4.94/arch/mips/boot/dts/ingenic
系统
kernel、rootfs 和 uboot之间的关系
- U-Boot 是引导加载程序,主要完成系统的初期引导工作。它会进行硬件初始化,然后从Flash、SD卡等外部存储中加载 Linux Kernel。
- Linux Kernel 是系统的内核,提供操作系统的核心功能。U-Boot会把内核映像加载到 RAM 中,并转交给内核控制权。
- Rootfs 是 root 文件系统,包含了 Linux 系统启动后需要的库、工具等文件。U-Boot同样会把 rootfs 从存储中加载到 RAM,以供内核挂载。
- 内核初始化完成后,会挂载 rootfs 为根文件系统,然后根据 rootfs 中的配置来启动系统服务,最终完成整个系统的启动。
- U-Boot主要在系统加电时执行,完成引导工作。内核和 rootfs 在系统运行时提供操作系统环境。
- U-Boot、内核和 rootfs 三者相互配合,将硬件系统引导起来,构成完整的 Linux 发行版。
- 开发时,会分别编译这三个组件,然后打包到存储介质中,实现可引导的嵌入式系统。 所以 U-Boot、Kernel 和 Rootfs 在嵌入式系统中有明确的分工,相互配合实现从系统加电到启动完成的整个过程。
uboot代码结构
- 启动代码(arch/arm/lib/crt0.S等):实现CPU和板级初始化,构建执行环境。
- 架构代码(arch/arm/):针对ARM等不同架构的底层支持代码。
- 公共库(lib/):提供字符串、内存相关的库函数。
- 驱动模型(drivers/):各种设备驱动,如串口、Ethernet、Flash等。
- 通用命令(cmd/):U-Boot命令行实现。
- 网络功能(net/):网络协议栈,如TFTP。
- 文件系统(fs/):文件系统驱动,如FAT。
- 加载Image(image/):镜像分析和加载。
- 板级支持(board/):针对特定开发板的定制代码。
- 通用核心(common/):初始化参数,环境变量,内存分配等。
- 入口点(main.c):主程序入口和命令行解析。
uboot
- uboot作用启动内核,设置一些环境变量
- uboot添加命令#define U_BOOT_CMD(_name, _maxargs, _rep, _cmd, _usage, _help)
- uboot基本命令
- reset:重新启动嵌入式系统。
- printenv:打印当前环境变量。
- setenv:设置环境变量,格式:setenv name value。
- saveenv:保存环境变量到nand中。
- sleep:延迟执行,格式:sleep N,可以延迟N秒钟执行。
- bootm:可以引导启动存储在内存中的程序映像。
- nand erase:擦除NAND,格式:nand erase addr1 count。
- nand write:下载的内存数据写入NAND,格式:nand write addr offset count。
- sf0 probe
- sf0 erase
- sf0 write
- uboot加载内核
- uboot的重要配置文件,默认配置在路径uboot/configs下,板级头文件在uboot/include/configs下
头文件由CONFIG_SYS_CONFIG_NAME宏配置。文件也可能没有默认配置文件,只需要头文件。 - uboot的nand的擦除,写入,读取命令在uboot/drivers/mtd/nand下实现